Caldisericum exile AZM16c01T (= NBRC 104410T)
Caldisericum exile AZM16c01T (= NBRC 104410T), isolated from a hot spring in Japan, which was the first cultivated microorganism that belongs to the candidate phylum OP5. Therefore, the new phylum name Caldiserica was proposed for the candidate phylum OP5 which have been indicated its existence by the environmental clone sequences in various
environments such as hot spring and pollutant associated places.
C. exile AZM16c01T is a filamentous-shaped, Gram negative thermophilic bacterium that grows anaerobically by reduction of sulfur compounds (thiosulfate, sulfite and elemental sulfur) to hydrogen sulfide, and grows optimally at 65 deg C. Yeast extract is essential for growth, but substrate compounds as electron donner is unknown experimentally.
The genome of C. exile AZM16c01T consists of a single circular chromosome of 1,558,103 base pairs (bp) in length with an average G + C content of 35.4%, and harboring 1,582 predicted protein coding sequences. Approximately 60% of the predicted proteins were most similar to Firmicutes, Dictyoglomi and Thermotogae especially which have the features of thermophilic, anaerobic and heterotrophic bacteria. More interesting was that approximately 9% of the predicted proteins were most similar to Archaea despite the genome size of C. exile AZM16c01T is small. The genome analysis revealed most biosynthetic pathways contained amino acids, cofactors, and nucleotides were lost in the microorganism, which suggests the role as the scavenger in the environment. The presence of genes with various ferredoxin oxidoreductases, heterodimeric sulfide dehydrogenase (Sud) and mbx operon may associate with sulfur reduction in C. exile AZM16c01T, which is similar to the single-enzyme respiratory system proposed in Pyrococcus belongs Archaea.
The genome sequence of C. exile AZM16c01T belonged new phylum Caldiserica would contribute to the clarification of biology and evolution of under thermophilic environment.
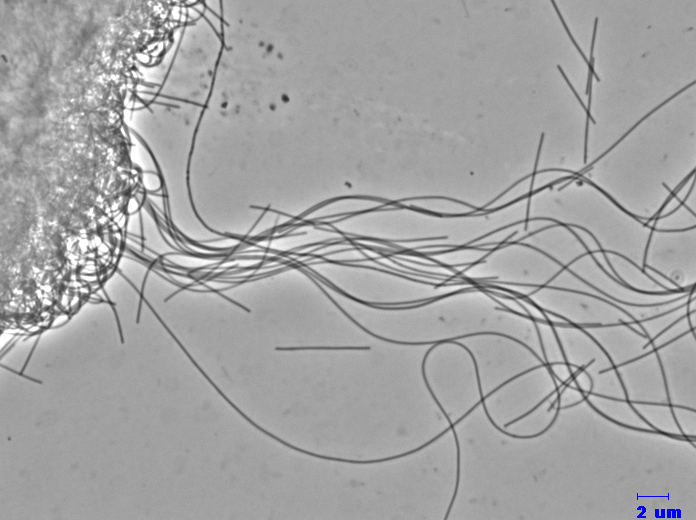
photo by Dr Mori (NBRC, NITE)
References:
- [1] Caldisericum exile gen. nov., sp. nov., an anaerobic, thermophilic, filamentous bacterium of a novel bacterial phylum, Caldiserica phyl. nov., originally called the candidate phylum OP5, and description of Caldisericaceae fam. nov., Caldisericales ord. nov. and Caldisericia classis nov.
- Mori K.,Yamaguchi K.,Sakiyama Y.,Urabe T.,Suzuki K.
Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 59 (2009) 2894-8 [PMID:19628600] - [2] First cultivation and ecological investigation of a bacterium affiliated with the candidate phylum OP5 from hot springs.
- Mori K.,Sunamura M.,Yanagawa K.,Ishibashi J.,Miyoshi Y.,Iino T.,Suzuki K.,Urabe T.
Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 74 (2008) 6223-9 [PMID:18776034]
| Genomic size: | 1,558,103 bp |
|---|---|
| The number of ORFs: | 1,582 |
| GC content: | 35.37% |
| Genome Database: | DOGAN |
| NBRC No. : | 104410 |
- Distribution of Our Microbial Genomic DNAs
- At the Biological Resource Center of the National Institute of Technology and Evaluation (NITE Biological Resource Center, an Incorporated Administrative Agency), we have been distributing the microbial genomic DNA.
Contact us
- Biotechnology Evaluation and Development Division, Biological Resource Center, National Institute of Technology and Evaluation
-
Address:2-49-10 Nishihara, Shibuya-ku, Tokyo 1510066, Japan MAP
Contact Form


